Context

Resolution
Here are given a code sequence and instructions to decode it.
From hex
We have to decode the code from hex, here is my code to do it:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import binascii
code = "32 69 31 73 34 69 31 73 31 35 64 31 6f 34 39 69 31 6f 34 64 31 6f 33 69 31 6f 31 35 64 31 6f 32 32 64 31 6f 32 30 64 31 6f 31 39 69 31 6f 37 64 31 6f 35 64 31 6f 32 69 31 6f 35 35 69 31 6f 31 64 31 6f 31 39 64 31 6f 31 37 64 31 6f 31 38 64 31 6f 32 39 69 31 6f 31 32 69 31 6f 32 36 69 31 6f 38 64 31 6f 35 39 64 31 6f 32 37 69 31 6f 36 64 31 6f 31 37 69 31 6f 31 32 64 31 6f 37 64 31 6f 35 69 31 6f 31 64 31 6f 32 64 31 6f 31 32 69 31 6f 39 64 31 6f 32 36 64 31 6f"
step1 = ''.join(code.split(" "))
step1 = binascii.unhexlify(step1).decode()
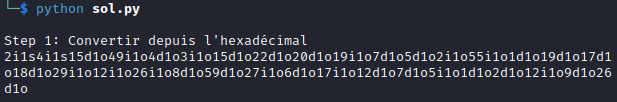
print("\nStep 1: Convertir depuis l'hexadécimal")
print(step1)
Here is the output:
Expand so that you no longer see numbers
Examples:
- 2i becomes ii.
- 4s becomes ssss.
My implementation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
step2 = ""
num = ""
for index in range(len(step1)):
if step1[index] in numbers:
num += step1[index]
try:
if step1[index + 1] not in numbers:
step2 += step1[index + 1] * int(num)
num = ""
index += 1
except:
pass
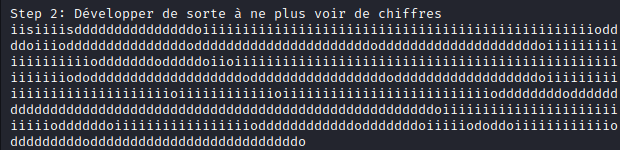
print("\nStep 2: Développer de sorte à ne plus voir de chiffres")
print(step2)
Here is the output:
Decode the DeadFish
The “Deadfish” is a simple programming language created as a joke or educational tool to demonstrate basic programming concepts. It is designed to be intentionally minimalistic and limited in functionality.
In Deadfish, there are only four commands, represented by the letters “i”, “d”, “s”, and “o”:
1
2
3
4
"i" (increment): This command increases a value by 1.
"d" (decrement): This command decreases a value by 1.
"s" (square): This command squares a value.
"o" (output): This command prints the value to the console.
The Deadfish language operates on a single accumulator, initially set to zero. Each command is executed sequentially, and the output command will display the value of the accumulator.
For example, let’s say we have the Deadfish code: “iiisdoso”. Here’s what each command does:
- “i”: Increment the accumulator from 0 to 1.
- “i”: Increment the accumulator from 1 to 2.
- “i”: Increment the accumulator from 2 to 3.
- ”s”: Square the accumulator, resulting in 9.
- “d”: Decrement the accumulator from 9 to 8.
- “o”: Output the value 8.
So, running the Deadfish code “iiisdoso” would display the number 8 as the output.
Deadfish is an example of an esoteric programming language, which means it’s not designed for practical use but rather for experimentation, amusement, or to explore unconventional programming concepts. Its simplicity and limited functionality make it an interesting starting point for learning about programming language design and the fundamentals of interpreting and executing code.
I found a repo online to decode the DeadFish: https://github.com/wanqizhu/deadfish-encoder
My code to decode the DeadFish:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
class Node():
def __init__(self, num):
self.num = num
self.edges = []
self.visited = False
nodes = [Node(i) for i in range(256)]
for i in range(1, 16):
nodes[i].edges.append((nodes[i-1], 'd'))
nodes[i].edges.append((nodes[i+1], 'i'))
nodes[i].edges.append((nodes[i**2], 's'))
for i in range(16, 255):
nodes[i].edges.append((nodes[i-1], 'd'))
nodes[i].edges.append((nodes[i+1], 'i'))
nodes[0].edges.append((nodes[0], 'd'))
nodes[0].edges.append((nodes[1], 'i'))
nodes[255].edges.append((nodes[255], 'd'))
nodes[255].edges.append((nodes[0], 'i'))
nodes[16].edges.append((nodes[0], 's'))
DP = {}
def BFS(nodes, s, t):
if (s, t) in DP:
return DP[(s, t)] + 'o'
for n in nodes:
n.visited = False
queue = [(nodes[s], '')]
while queue:
v, path = queue.pop(0)
v.visited = True
if v.num == t:
DP[(s, t)] = path
return path + 'o'
for (node, c) in v.edges:
if not node.visited:
queue.append((node, path+c))
DP[(s, node.num)] = path+c
# BFS(nodes[13], nodes[127])
def encode(s, start=0):
""" Encodes input string s into deadfish """
targets = [start] + [ord(c) for c in s]
out = ""
for i in range(len(s)):
out += BFS(nodes, targets[i], targets[i+1])
return out
def decode(s, accumulator=0):
out = ""
for cmd in s:
if accumulator == 256 or accumulator == -1:
# Overflow, reset accumulator
accumulator = 0
# Process input
if cmd == 'i':
accumulator += 1 # Increment
elif cmd == 'd':
accumulator += -1 # Decrement
elif cmd == 'o':
out += chr(accumulator) # Output
elif cmd == 's':
accumulator *= accumulator # Square
return out, accumulator
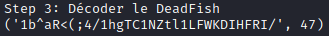
step3 = decode(step2)
print("\nStep 3: Décoder le DeadFish")
print(step3)
Here is the output:
Convert from Base 85
For this step, we just use the base64 library:
1
2
3
step4 = base64.a85decode(step3[0]).decode()
print("\nStep 4: Convertir depuis la Base 85")
print(step4)
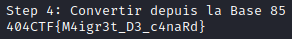
We’ve got the flag !